The Uniqueness of Murata’s Crystal Devices
Murata has developed a number of products using piezoelectric effect. Crystal devices also use the piezoelectric effect of quartz crystal. The application of technologies accumulated in the development of past piezoelectric products to quartz crystal has now helped us use the excellent properties of quartz crystal in the development of new products of unprecedented additional value.
Having provided CERALOCK ceramic resonators for years, Murata has now developed new quartz crystals in a reduced size to cater to the demand for even higher precision clocks. Volume production of the HCR XRCGB series began in 2009 for the general consumer market. In 2013, Murata began volume production of the HCR XRCHA-F-A series for automotive onboard ECUs, and later on, the XRCMD series for applications in wireless communication. Their most characteristic feature is the adoption of unique Cap Chip structure in the package. The Cap Chip structure has been used in CERALOCK for years. The structure helps us accomplish higher productivity and supply stability. The Cap Chip structure uses a ceramic plate and a metal cap. The toughness of the metal allows the cap to have an extremely thin wall while maintaining sufficient strength. The Cap Chip structure can therefore have a greater inner surface area, allowing us to install a crystal blank of larger surface area. For this reason, the new products will be able to reduce the equivalent series resistance (ESR) more easily than currently available common quartz crystals of the same size. The lower the ESR, the easier the matching between quartz crystals and ICs. This will be a great advantage in circuit design. To seal the metal cap to the ceramic plate, HCR uses the adhesive that has been used in CERALOCK. Resin sealing has the advantage of being lower in cost, but it has been avoided in quartz crystals, because, in a highly humid environment, the resin sealing cannot prevent water vapor from permeating the seal and quartz crystals are vulnerable to vapor condensation. Murata, however, found that this disadvantage of resin sealing could be circumvented under particular conditions: The constraint of limited space volume within a package suppresses the volume of permeating water vapor, thereby minimizing the amount of vapor condensation. Murata took advantage of this phenomenon by applying it to the products (Patent No. 4458203). Furthermore, using the structural property that allows the permeation of water vapor, Murata established a method of detecting and eliminating particles, one of the causes of improper oscillation, in the production line (Patent No.4998620). With various other strategies in addition to the one just mentioned, Murata has reduced the ratio of particles inside the sealed structure of HCR.
The XRCMD series, on the other hand, accomplishes hermetic sealing, using fusion bonding of an alloy in the seal between the ceramic plate and the metal cap. The structure, in addition to having the advantages inherited from the Cap Chip structure that readily accomplishes low ESR, can reduce the temperature dependence of frequency as well as the change, or more specifically, the deterioration of the frequency characteristics over time, allowing the devices to achieve the frequency precision required for wireless communication clocks.
Murata has been promoting further miniaturization and precision improvement of these quartz crystals that have the characteristic Cap Chip structure. Murata has been trying to integrate other passive and active components into these products. With this kind of unique approach, Murata’s challenge to develop new timing devices will be never-ending.
HCR XRCGB series
XRCMD series
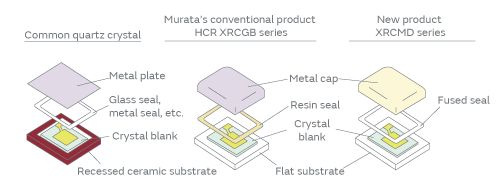
Structural comparison of various quartz crystals