11/10/2020
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
President: Norio Nakajima
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (hereinafter, “Murata”) commissioned Nara Medical University to research the effectiveness of ozone gas generated by Murata’s Ionissimo technology *1 (hereinafter, “the products”) in inactivating the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2*2). The ozone gas generated by Ionissimo technology was proven to be effective in inactivating the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). This confirmation of Ionissimo technology effectiveness was conducted using an airtight testing chamber; its effectiveness in an actual usage environment, outside the testing chamber, has not yet been tested.
Testing contractor
Nara Medical University, Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, School of Medicine (Professor Hisakazu Yano and Professor Ryuichi Nakano)
Confirmation of effectiveness of Ionissimo technology in inactivating the novel coronavirus
Data
• Testing period: August to September 2020
• Subject: Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
Methodology
• 20 μl of fluid containing the virus was applied to a petri dish and left to stand until dry.
• The test piece containing the virus was left to stand in a 6.7-liter airtight chamber and exposed for a fixed period of time to ozone generated by the Ionissimo technology and propelled by a fan.
• Only a single test piece was placed in the chamber and removed when the reaction time had elapsed.
• After the test piece was removed, the procedure was reset and a new test piece placed in the chamber, with the reaction time starting again from 0 minutes.
• After the reaction time had elapsed, 2 ml of SCDLP culture medium*3 was dripped onto the test piece, and a cell scraper was used to collect the virus.
• The collected fluid was used to infect Vero E6/TMPRSS2*4 cells, and the virus infectivity*5 (PFU/mL) was measured using a plaque assay*6.
• Test pieces not exposed to ozone were used as a control.
• The test was carried out three times in the following environment: humidity 50.0% to 59.7%; and temperature 19.6°C to 21.8°C.
• The ozone concentration value was measured beforehand with no test piece present.
Results
It was confirmed that at least 99.9% of the virus became inactive following exposure for 120 minutes to a concentration of 0.1 ppm, which is the acceptable ozone concentration designated by the Japan Society for Occupational Health.
Note: The present confirmation of effectiveness was conducted using the products in a testing chamber environment and does not indicate effectiveness in an actual installation/usage environment.
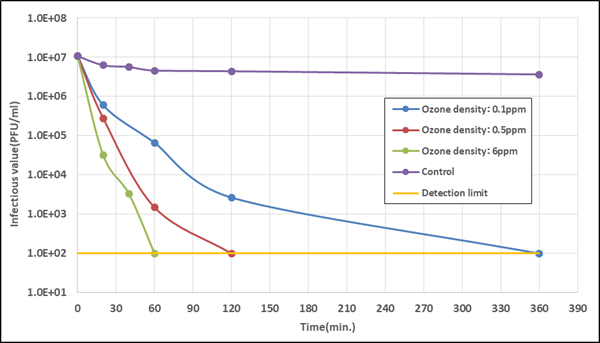
Figure 1. Change in virus infectivity due to ozone
Actual measured virus infectivity value (average where n = 3)
Note: Control (violet line in Fig. 1): air environment without ozone exposure
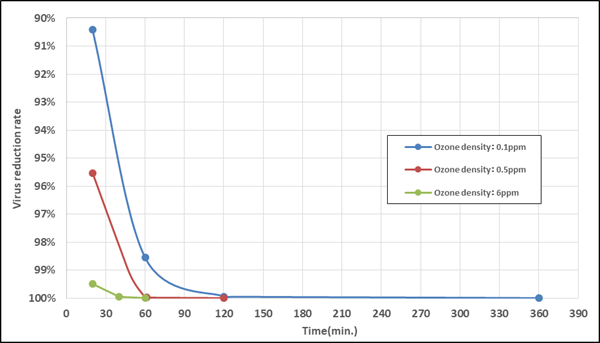
Figure 2. Virus reduction rate due to ozone
Note: The reduction rate was calculated from the virus infectivity results. A reduction rate beyond the detectable limit is indicated as > 99.997%.
Table 1. Virus reduction rate due to ozone
| Ozone concentration |
0 min. |
20 min. |
40 min. |
60 min. |
120 min. |
360 min. |
720 min. |
| 0.1 ppm |
– |
90.425% |
– |
98.550% |
99.939% |
> 99.997% |
> 99.997% |
| 0.5 ppm |
– |
95.531% |
– |
– |
> 99.997% |
– |
– |
| 6.0 ppm |
– |
99.492% |
99.941% |
> 99.997% |
– |
– |
– |
Notes
1. Ions are generated by applying a high-voltage direct current to needle-shaped electrodes (metal wires about 70 µm thick). The ions are electrically charged, and the charge catches tiny floating particles by Coulomb force. At the same time, Ionissimo technology have electrodes formed on a ceramic board surrounding the needle-shaped electrodes, and these generate ozone. The oxidizing power of the ozone effectively disinfects and eliminates odors.
2. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, abbreviated as SARS-CoV-2. It causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and is related to the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV).
3. A fluid culture medium used to collect the virus.
4. A type of cell susceptible to infection by novel coronavirus.
5. The number of virus particles that are infectious to cells.
6. A method used to isolate or quantify a virus.
Changed to April 12, 2021
Murata in Brief
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a worldwide leader in the design, manufacture and sale of ceramic-based passive electronic components & solutions, communication modules and power supply modules. Murata is committed to the development of advanced electronic materials and leading edge, multi-functional, high-density modules. The company has employees and manufacturing facilities throughout the world.
For more information, visit Murata's website